There have been many advancements in hair loss treatments over the last 30 years. The most recent methods for treating hair loss are stem cell-based treatments like TrichoStem® Hair Regeneration and platelet-rich plasma (PRP).
Traditional Hair Loss Treatments
Hair transplant
A hair transplant is a procedure performed on individuals who have suffered significant hair loss, thinning hair, or baldness. Hair is transplanted from donor area or the area resistant to hair loss from the sides or back of the head. The hair is transplanted onto areas of the scalp that are mostly devoid of hair, typically the front. Hair transplants are suitable for people who have areas of scalp that have been completely bald (where the skin is smooth and there are no thinning hairs) for 3-5 years, when hair thinning treatments can’t help no longer viable hair follicles.
In cases of hair thinning and bald patches, hair transplantation must be done extremely carefully. Transplanting hair grafts too close to existing hair can damage existing hair follicles, which can lead to more hair being lost than replaced.
There are 2 types of hair transplant procedures: the follicular unit transplant (FUT) and follicular unit extraction (FUE). The procedures are practically identical in placement of hair grafts, but differ in how grafts are harvested from the patient.
Follicular Unit Transplant (FUT)
Follicular unit transplantation (FUT) is a more “traditional” hair transplant method, and is regarded by many hair transplant doctors as the most effective in restoring better hair density and yielding higher quality hair grafts. The FUT involves the excision of a thin strip of skin at the lower part of scalp, at the back of the head, which is why it is also known as the strip method. Groups of 1-4 follicles, known as follicular units, are carefully removed under a microscope. These hair grafts are then ready for transplant. The hair grafts are placed in an implanter device. During surgery, the surgeon or technician has several implanter devices in hand, with an assistant continuously refilling the implanters. Anywhere from 1500-3000 grafts are harvested and transplanted in session, which depends on the density of the donor area. As many as 4000 grafts can be harvested in a session, but these are rare cases.

The donor area prior to the strip excision. This narrow band of hair is genetically resistant to the effects of DHT, so hair from this area, even if transplanted, will not thin.
Excising the strip of skin is both a significant advantage of the FUT method, as well as what many consider its disadvantage. Using the strip of skin, follicular units can be removed intact completely intact, so fewer grafts are damaged at the root (transection). Since the strip is removed fairly quickly, the patient is not subjected to long hours surgery.
FUT Effectiveness:
It is generally believed by hair transplant surgeons that FUT yields more and better quality grafts than any other hair transplant method. Since the strip is removed from the body, follicular units can be harvested with the roots (dermal papillae) intact and healthy. The strip only yields hairs that are genetically-resistant to the effects of DHT, so transplanted hairs are not prone to hair thinning.
While 1500-3000 grafts sound like a lot, keep in mind that hair count at its peak in the early teens number about 100,000. When hair loss is first noticed, about half of hair is already gone.
FUT Treatment Duration
The FUT takes about 3-4 hours, while the alternative FUE procedure typically takes at least twice that long.
FUT Limitations
It’s important to that any hair transplant, regardless of method, will ever replace the amount of hair lost.
FUTs, like all hair transplants, do not stop or prevent more hair from being lost.
The most significant difference of the FUT is the donor strip area where the hair grafts are harvested. This area at the back of the head has the potential to form a scar. Advanced wound healing and cosmetic surgery closure can potentially minimize the strip scar. Hair transplantation being performed by a wide variety of doctors and specialties results in various levels of surgical skill and experience with cosmetic procedures. It is the desire to avoid an obvious strip scar that lead to the development of other hair transplant techniques.
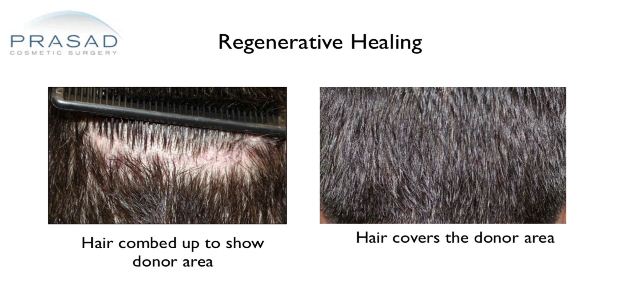
The advantage of a cosmetic surgeon with knowledge of advanced wound healing performing hair transplants can be seen in donor strip healing. Dr. Prasad applied extracellular matrix, the same active ingredient in the TrichoStem® Hair Regeneration hair restoration treatment, for regenerative healing of the donor area.

The donor strip scar after an FUT is performed by another practice, where the scar actually widened.
FUT Side Effects
Temporary swelling and pain, and possible loss of adjacent hairs due to trauma of surgery (shock loss). Temporary scabbing from surgery.
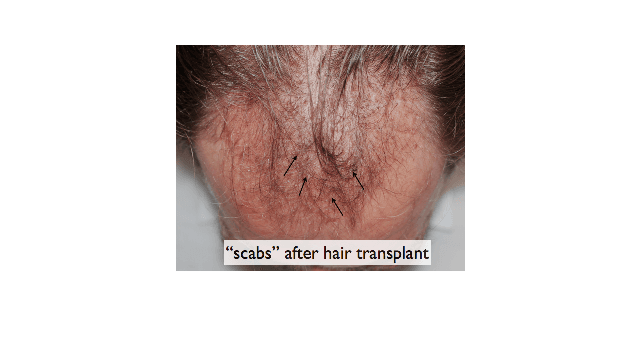
Temporary scabbing after a hair transplant.
Follicular Unit Extraction ( FUE)
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) came about to do away with the donor strip and its possible scar. The FUE uses various methods to extract grafts directly from the patient’s head so a strip of skin is not excised: punch grafts, robotic graft harvesters, extractors, forceps, isolators, and spreaders.
The FUE does not involve a long strip to avoid scarring, but it can create numerous smaller scars throughout the back of the head.
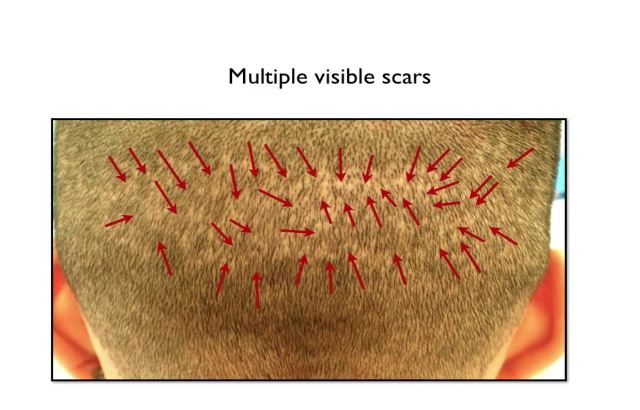
The FUE came about to avoid the single, large strip scar of the FUT, but instead it was replaced by smaller, numerous scars.
Main Advantage of the FUE
The FUE is the preferred method of hair transplants for only one real reason – avoidance of the surgical strip. Scar formation can be a problem with other hair restoration practices, but Dr. Prasad’s experience with healing the donor area using cosmetic surgery closure and advanced healing materials does not make the strip excision a major factor.
Disadvantages of the FUE:
Less Grafts
The FUE is a more modern procedure, but does have many disadvantages compared to the FUT, with the main one being numbers of grafts. More grafts can be harvested using the FUT from the donor strip, than using the FUE technique. The FUT takes ALL the grafts from a small area, while the FUE takes SOME grafts from a wider area. The reason FUEs take grafts from a wider area is that it can’t get enough grafts from the narrow true donor area.
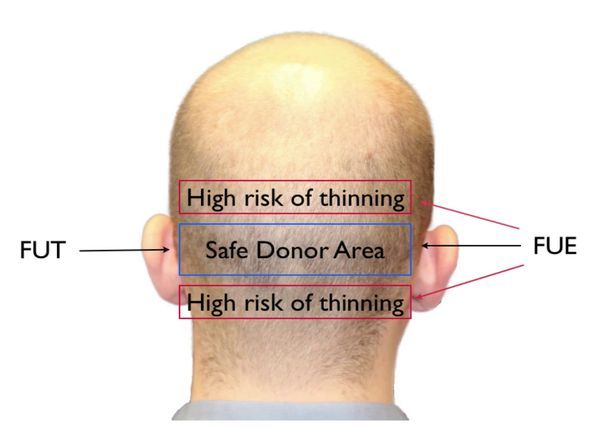
The FUT takes the entire strip at the donor area, which yields only hairs genetically resistant to hair thinning. Since the FUE avoids taking all the hair from the strip, it harvests hair outside the permanent zone, which can be subject to the effects of DHT and thin.
Hair Graft Thinning and Survival
Since the FUE method takes grafts outside the genetically resistant to thinning donor area, it takes hair grafts that may be sensitive to thinning effects of DHT. FUE transplants will need even more repeat transplant sessions because not only does native hair continue to thin after a transplant, but even surviving transplanted hair could also thin. Having thinned hair grafts is even more likely during “megasessions” that promise 4000 or more grafts, where patients are so enticed by the large number of grafts, but don’t realize the grafts can thin and may be lost as well.
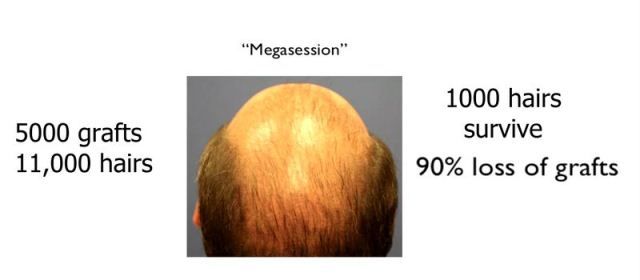
Hair restoration practices that promote themselves as higher in graft count should be approached with caution. Survival of grafts, and grafts that are not prone to thinning are more important factors.
Damaged Hair Grafts
The most important part of the hair and the hair graft is its root called the dermal papilla. The dermal papilla with some surrounding soft tissue must remain intact for the graft to take and grow. With the FUT method, the skin surrounding the graft can be precisely cut and spliced under a microscope to ensure the dermal papillae are left intact. However, with the FUE method, splicing can’t be done because the graft is taken from live patient’s head. Use of tools such as graft punches can cut the dermal papillae (medically known as as transection). Other FUE tools such as forceps can stretch and damage the dermal papillae, making the graft unvialbe. Any hair restoration doctor that performs the FUE will say that transection will happen to a varying degree. Losing up to 30% of FUE grafts due to transection is common.
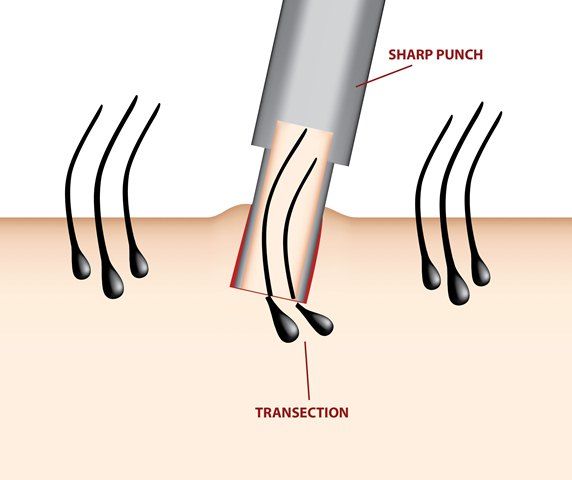
It is an industry standard that FUEs are more prone to damaged grafts because of the inaccurate way harvesting is done directly from the patient , rather than indirectly from an excised strip of the FUT for more accurate harvesting
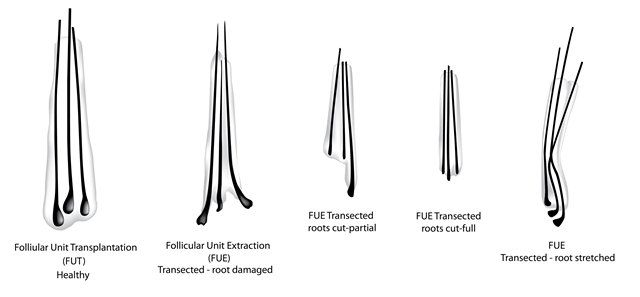
Comparing healthy hair grafts from the FUT, and possible permutations of damaged hair grafts seen in the FUE method. If the roots (dermal papillae) are damaged, the hair grafts won’t take and grow.
Longer Surgery
The FUE procedure is generally at least twice as long as the FUT procedure as the patient needs to be face down for a long extraction process. FUEs lasting beyond 10 hours are common. Since it is such a long procedure, a team of the doctor(s) and the technicians are needed to keep fresh eyes and hands on the surgery. The doctor does extract the grafts and designs the hair pattern for placement, but technicians can and do place the grafts alongside the surgeon. The doctor is in full control of the procedure the entire time. Longer surgery can also take a toll on the patient.
Higher Cost
FUE will always be a more expensive surgery compared to the FUT because of the longer time needed for the procedure. A longer procedure means a higher professional fee for the doctor, more anesthesia and medication, larger staff needed, and longer operating room time.
FUE Effectiveness
Grafts from FUE transplants have higher incidence of not surviving to the growth stage, and for thinning among grafted hairs when compared to FUT transplants.

Even after 4 hair transplants, hair can still thin. Transplanted hair that was harvested outside the permanent zone which is a common practice in FUEs can also thin.
FUE Treatment Duration
At least twice as long as a similar FUT procedure. Surgeries over 10 hours long are common.
FUE Side Effects
Smaller scars over a wide area at the back of the head.
Temporary pain, soreness and scabs following surgery.
Hair Loss Drugs
Minoxidil (Rogaine or Regaine)
Minoxidil was a drug first used to treat blood pressure and based on side effects, later used to treat hair loss. Minoxidil is a topical application used directly on the scalp, and can be used by men and women. It is most popularly sold under the brands Rogaine and Regaine in 2% concentrations for both men and women, and 5% for men. Minoxidil works by extending the hair growth cycle, and delaying the hair shedding cycle, so more hair is present on the head at a given time. How the drug achieves this is not exactly known, but it is believed to be linked to its blood circulation properties. Minoxidil does not stop or delay hair thinning, nor does it make hair thicker.


Minoxidil is most commonly sold under the brand names Rogaine and Regaine. The extra strength version is a 5% concentration, while the regular strength version is a 2% concentration.
Minoxidil Effectiveness
Minoxidil can make hair seem thicker, or have more hair on the head due to delayed shedding and prolonged growth.
Effects of minoxidil can last if twice daily application is adhered to, with effects disappearing soon after use is discontinued. Minoxidil does not work on everyone.
Minoxidil Treatment Duration
Effects of minoxidil can be seen after regular application once or twice daily, usually three to six months to a year after initial application.
Minoxidil Side Effects
- Irritation, redness, and itchiness of the scalp
- Dryness and flaking of the scalp
- Greasy hair, but this problem has been reduced with its lighter foam version
Minoxidil’s blood pressure effects can lead to:
- Increased heart rate
- Chest pains
- Headaches and dizziness
- Difficulty of breath
Finasteride (Propecia)

Finasteride is most commonly sold under the brand name Propecia.
Finasteride, sold under the brand name Propecia, is an inhibitor of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase. Finasteride is an oral pill taken daily, in a 1 mg concentration for hair loss. A 5mg concentration of finasteride is used to treat enlarged prostate. 5-alpha reductase converts the hormone testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which affects people with DHT-sensitive hair follicles. Hair follicles affected by DHT grow progressively thinner with each hair growth cycle, and eventually disappear if left untreated. By blocking the conversion of testosterone to DHT, finasteride can reduce hair thinning and thicken hair. Depending on the study , it is often perceived by professional who prescribe finasteride that it works in about half of male patients. Other studies show higher rates of benefit. This suggests that there are other hair loss causes beyond DHT. Finasteride is only prescribed to males.
DHT-sensitivity is the main cause of pattern hair loss among men and women, and is medically known as androgenetic alopcecia. About 95% of all hair loss cases are cases of androgenetic alopecia. DHT disrupts the normal hair growth cycle from the roots of the hair follicles (dermal papillae). Hair follicles have androgen (hormone) receptors, and many people have scalp hair sensitive to the hormone DHT.
Finasteride Effectiveness
According to a 5-year independent study, Finasteride works in about half of the men who showed visible increased hair growth.
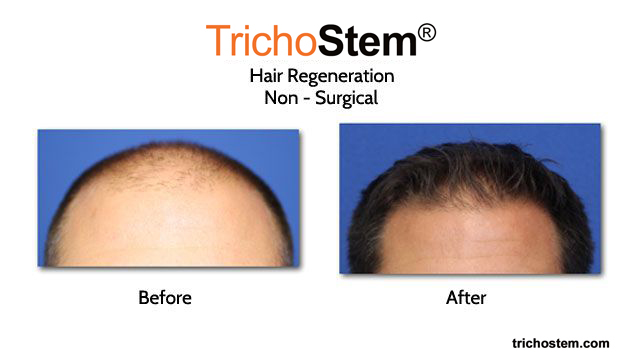
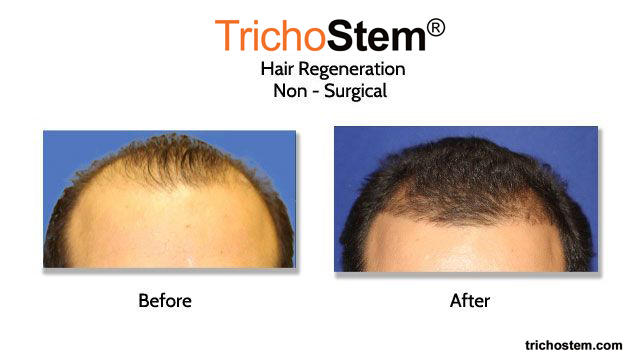
Two young males with limited response to finasteride as seen in their before pictures have significant hair growth with TrichoStem® Hair Regeneration with one, non-surgical treatment.
Treatment Duration
Effects of finasteride on thinning hair usually manifests in up to a year after therapy starts. The pill must be taken daily and in its full 1mg form to see results. After cessation of the drug, hair will revert to rate of thinning prior to finasteride therapy.
Side Effects:
Challenges to finasteride therapy include consistent compliance and potential sexual side effects. In one of the first finasteride studies, about 2% of men in both the active drug group and the placebo group reported sexual side effects. Side effects have been reported even years after cessation of the finasteride. These include:
- Decrease in sexual interest
- Decrease in sexual performance
- Erectile dysfunction
- Compromised quality of semen
- Compromised quantity of semen
- Infertility
- Impotence
To learn more about TrichoStem® Hair Regeneration, a significant advancement in hair loss management, contact us in Manhattan, New York City at (212) 265-8877, Garden City, Long Island at (516) 742-4636, at our new location in Vienna, Virginia at (703) 356-1336, or fill out the contact form below so we can begin helping you with your hair loss.
